e202582 Motor: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: e202582 Motor: A Comprehensive Overview
- Yorkshire Water Business Plan 2025: A Comprehensive Overview
- 2025 Jeep Renegade: A Compact SUV With Off-Road Prowess
- Global LF Yield 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook
- ICC Champions Trophy 2025: Teams, Format, And Schedule
- 2025: A Year Of Cinematic Delights
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to e202582 Motor: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about e202582 Motor: A Comprehensive Overview
e202582 Motor: A Comprehensive Overview

Introduction
Electric motors are ubiquitous in modern society, powering everything from appliances to vehicles. Among the various types of electric motors, the e202582 motor stands out for its compact size, high efficiency, and versatility. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the e202582 motor, exploring its design, operating principles, applications, and advantages.
Design and Construction
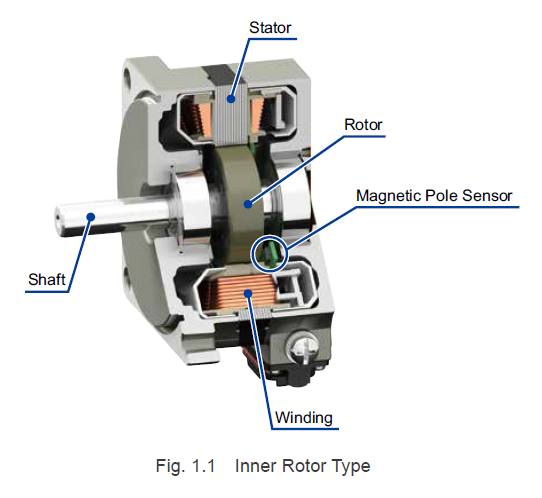
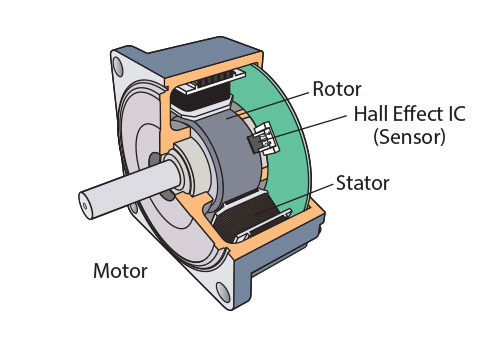
The e202582 motor is a brushless DC (BLDC) motor, which means it uses a permanent magnet rotor and a stator with three or more windings. The stator windings are typically arranged in a three-phase configuration, with each phase being connected to a separate electronic commutation circuit.
The rotor of the e202582 motor is made of a high-strength rare-earth magnet, such as neodymium or samarium cobalt. The magnet is typically cylindrical in shape and has a series of evenly spaced poles.
The stator of the e202582 motor is made of laminated steel and has a series of slots that accommodate the stator windings. The windings are typically made of copper wire and are connected in a specific sequence to create the desired magnetic field.
Operating Principles
The e202582 motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an electric current flows through the stator windings, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the rotor, causing the rotor to rotate.
The direction of rotation of the e202582 motor is determined by the sequence of the electric current flowing through the stator windings. By changing the sequence of the current, the direction of rotation can be reversed.
Control and Commutation
The e202582 motor is typically controlled using an electronic commutation circuit. This circuit provides the necessary electric current to the stator windings in the correct sequence to produce the desired rotation.
The electronic commutation circuit can be implemented using a variety of methods, including Hall effect sensors, optical encoders, or sensorless control algorithms.
Applications
The e202582 motor is a versatile device that can be used in a wide range of applications. Some of the most common applications include:
- Industrial automation
- Robotics
- Medical devices
- Aerospace
- Automotive
Advantages
The e202582 motor offers several advantages over other types of electric motors, including:
- Compact size: The e202582 motor is highly compact, making it suitable for applications where space is limited.
- High efficiency: The e202582 motor has a high efficiency, which means it consumes less energy to produce the same amount of torque.
- Low noise: The e202582 motor operates with very low noise, making it suitable for applications where noise is a concern.
- Long lifespan: The e202582 motor has a long lifespan, which reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
Conclusion
The e202582 motor is a compact, efficient, and versatile electric motor that is suitable for a wide range of applications. Its high efficiency, low noise, and long lifespan make it an excellent choice for applications where performance and reliability are critical. As the demand for electric motors continues to grow, the e202582 motor is expected to play an increasingly important role in various industries and applications.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into e202582 Motor: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!